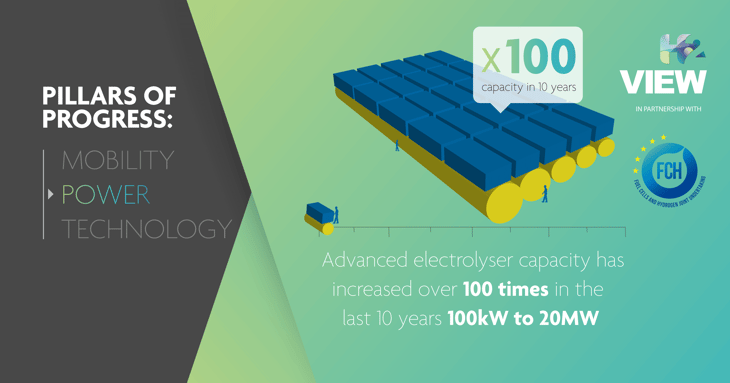
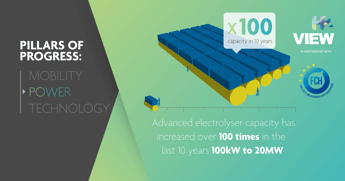
Green hydrogen produced by harnessing surplus electricity from wind and solar sources is an important back-up power solution.
Using excess electricity from renewables to split water molecules via electrolysis, the resulting green hydrogen can be stored and used in fuel cells to supply power as needed or can be fed to industry or transport for greening these sectors.
For green hydrogen to be used in such applications, electrolysis technology must become flexible enough to be coupled with renewables in real world conditions, and costs need to be cut.
... to continue reading you must be subscribed